Functionally and Geometrically Ordered Ti Armor
Ballistic Tests for Ti Composite Armors
1: Material Properties
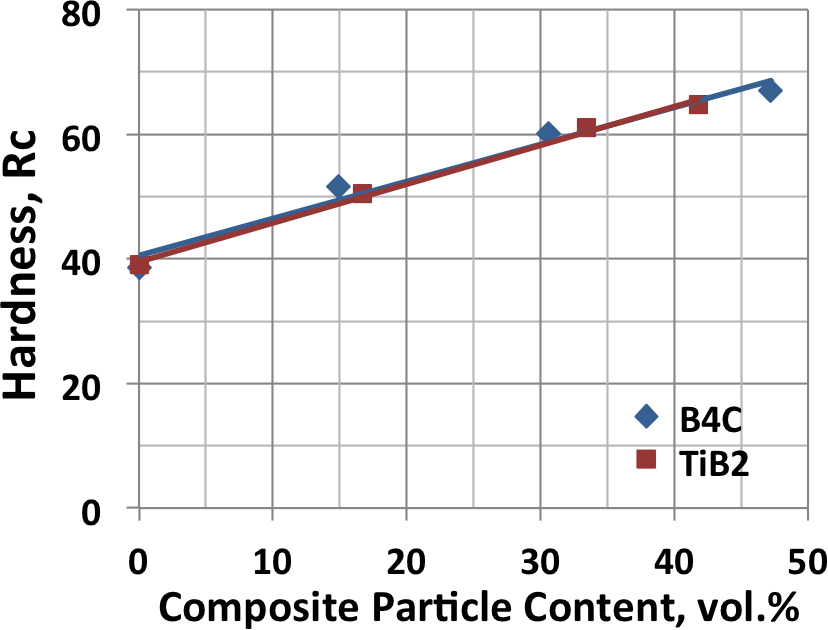
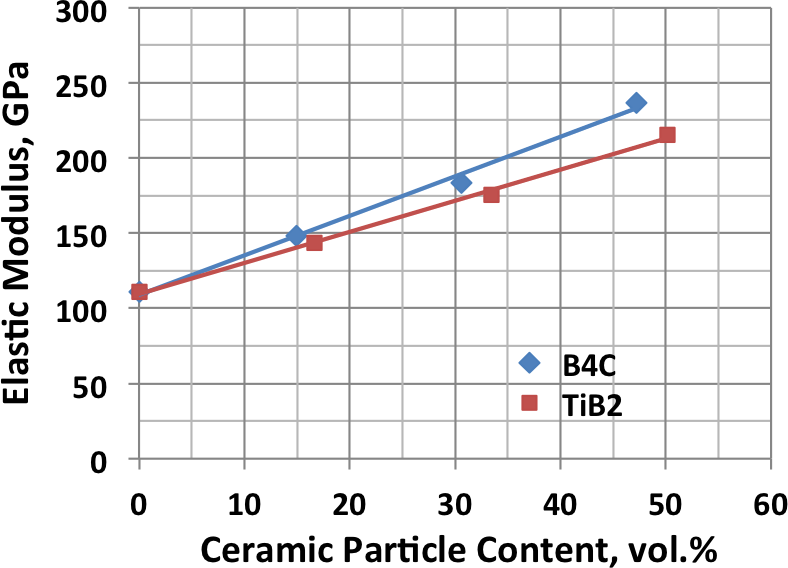
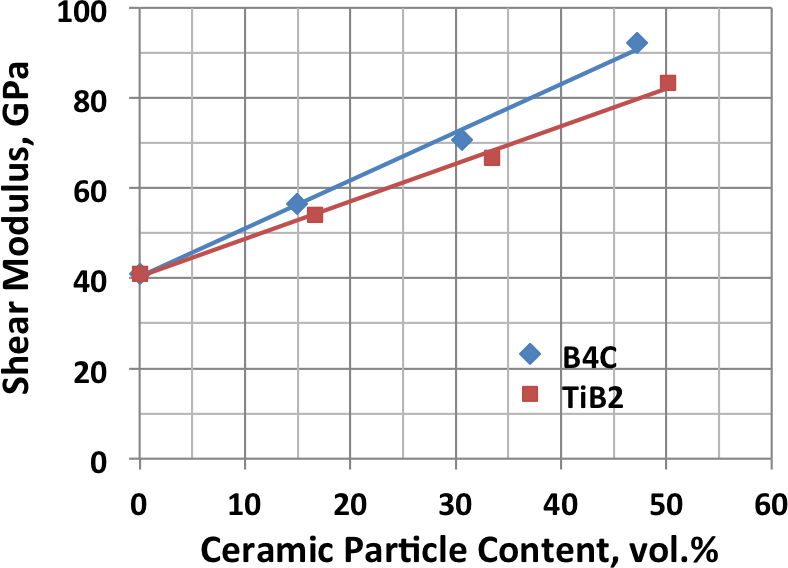
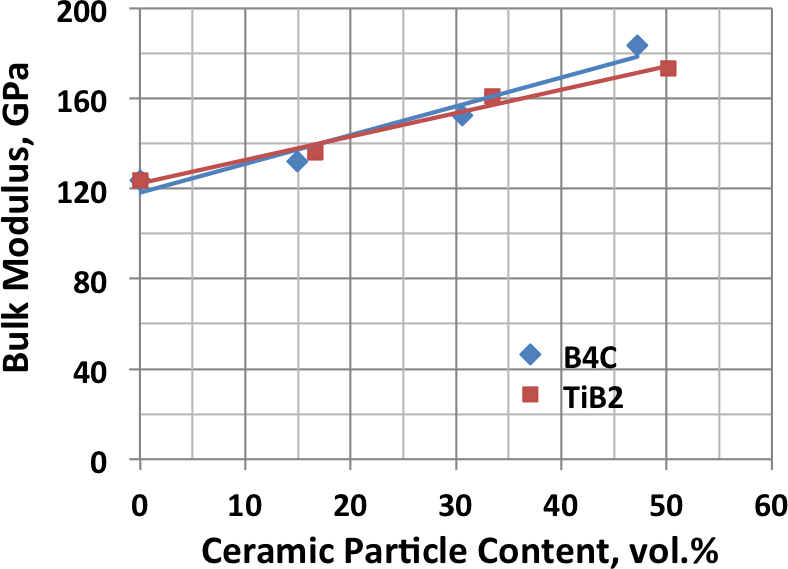
Various armor configurations have been fabricated using powder metallurgy processes to combine metal and ceramic materials. Because of the flexibility of powder processing, there is essentially no limit to the complexity of structures that can be produced. The physical properties of blended and consolidated titanium and ceramic powders can vary broadly as illustrated by the following examples showing the range of hardness and elastic modulus that has been demonstrated.
|

|
|
|
|
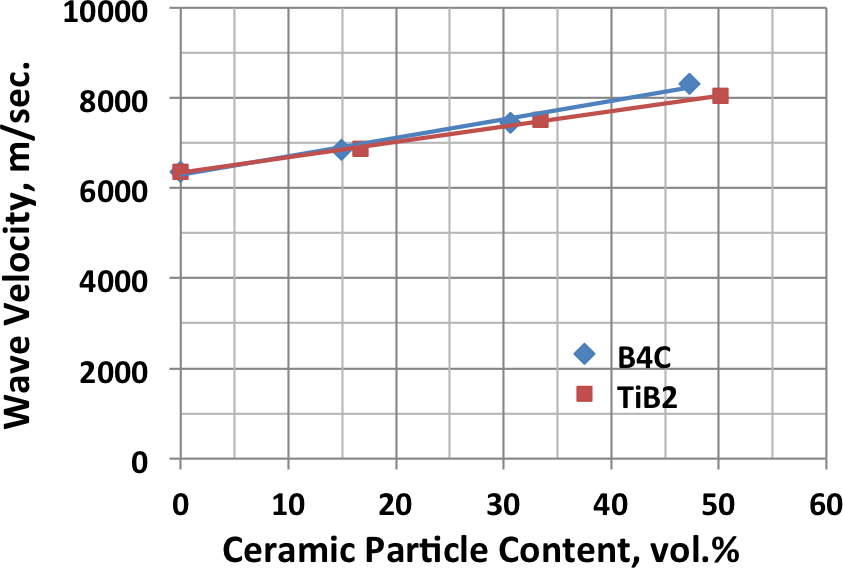
|
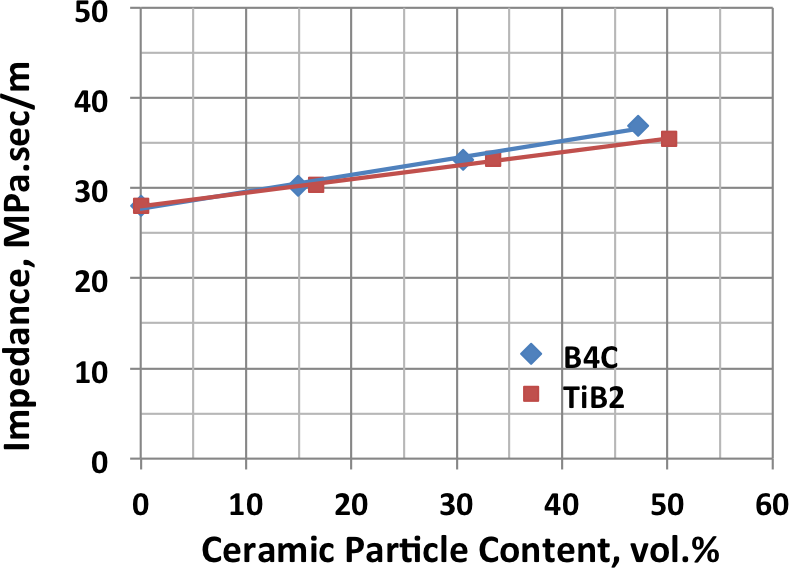
|
2: Ballistic Tests
Ballistic testing was conducted on a variety of graded and geometrically complex armor tiles have been tested versus the .30 cal. APM2 armor piercing round.
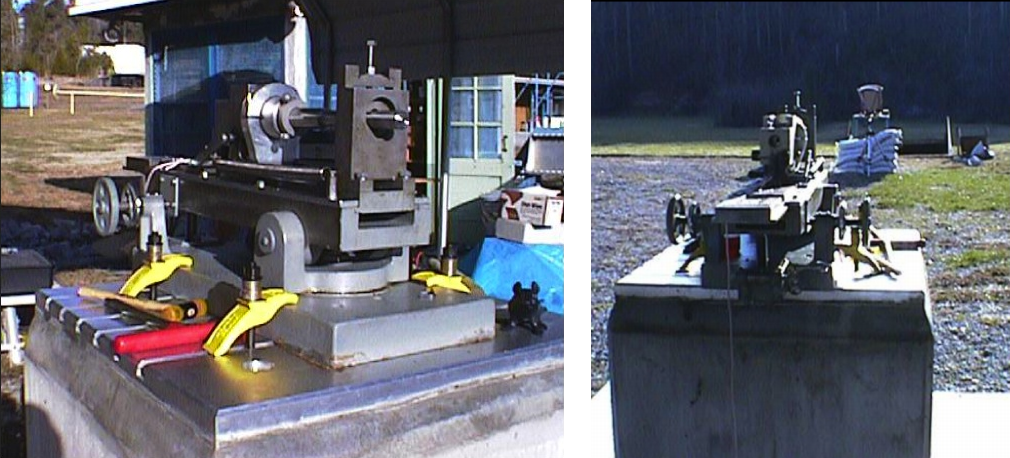
|
|
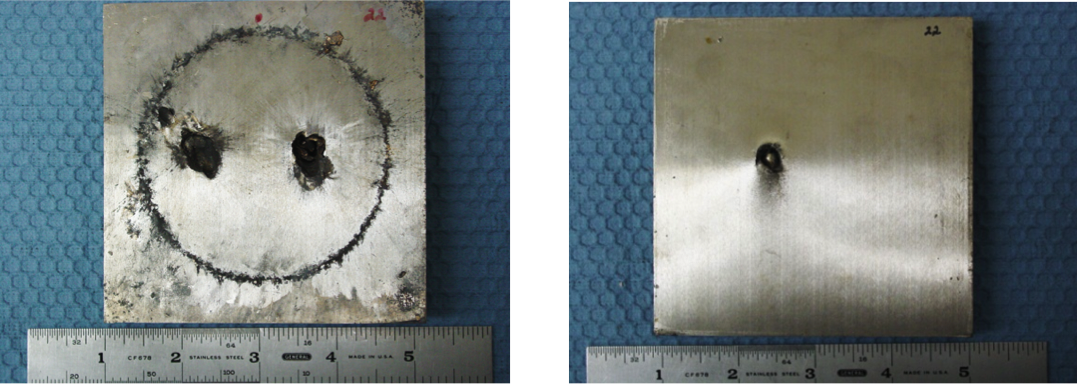
The test results were compared to both conventional wrought titanium armor and monolithic powder metallurgy titanium plates. Examples of armor tiles that underwent ballistic testing are shown in the figures below. Also shown is a graphical summary of the test results for the various types of armor that were tested.
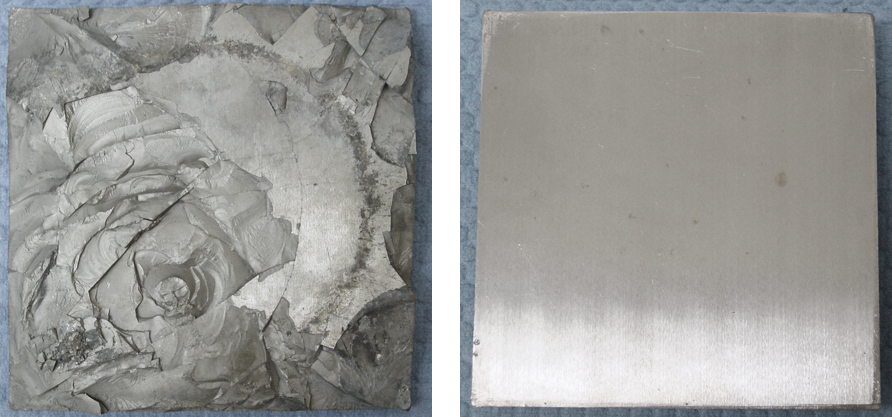
|
Functionally graded armor tile after ballistic testing. Left: The impact surface showing spallation and Right: The exit surface showing no damage. The tile had a ballistic mass efficiency, Em, of 1.76.
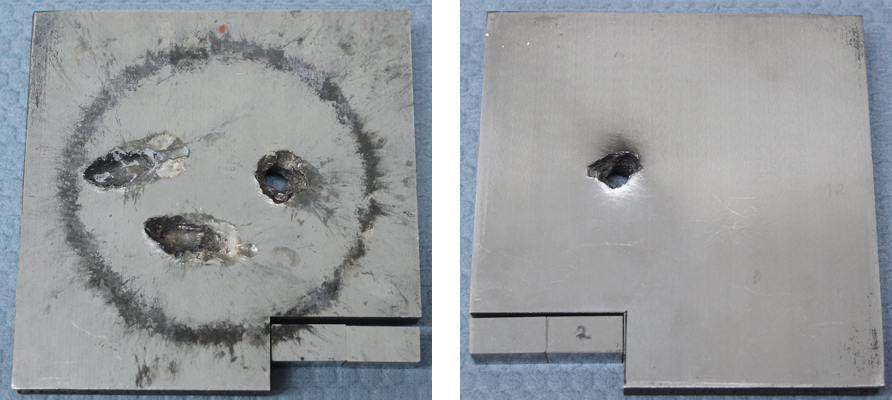
|
Composite tile with geometrically complex interfaces (see cross-section) after ballistic testing with various impact velocities. Impact surface (left) and exit surface (right). The tile had a mass efficiency, Em, of 1.67.
Comparison of the ballistic mass efficiency of various armor tile materials and structures
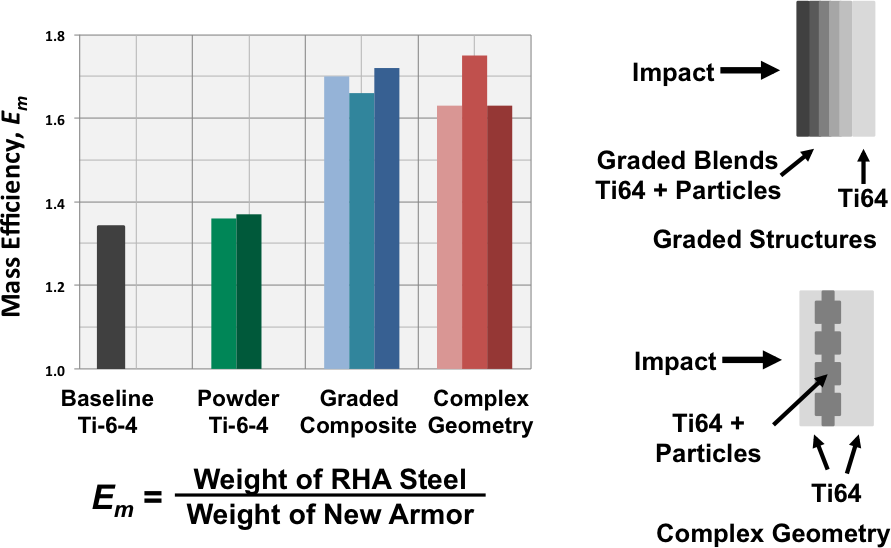
|